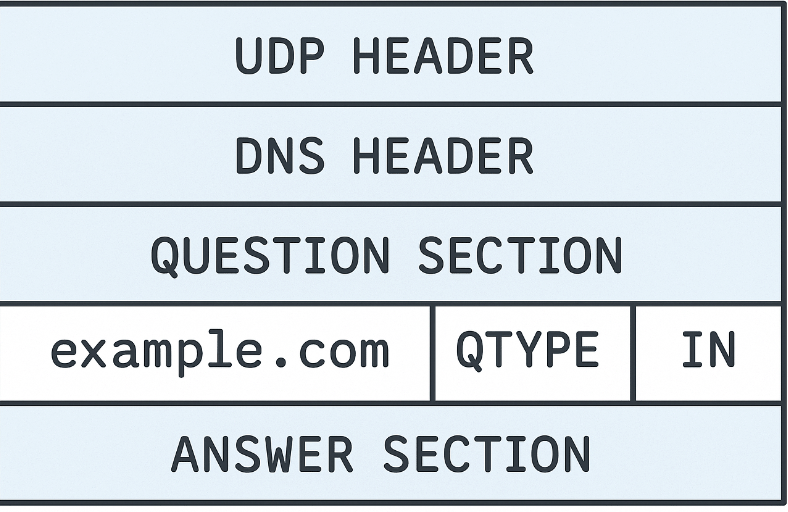
What is DNS?
DNS is a protocol that translates domain names into numerical IP addresses, allowing computers to locate and communicate with each other over the Internet.
Client request:
A user enters a domain name in their browser or application.
Recursive resolver:
The user’s device (or a local DNS server) sends a request to a recursive resolver, which acts as an intermediary.
Root server:
The resolver first queries a root server, which redirects it to the appropriate Top-Level Domain (TLD) server, such as .com or .org.
TLD server:
Then, the resolver queries the TLD server, which points to the authoritative server for the specific domain.
Authoritative server:
Finally, the authoritative server provides the IP address associated with the requested domain name.
Response:
The IP address is returned through the same chain of servers back to the user’s device, allowing them to connect to the website.